Based on the bootEGA results, this function
computes and plots the number of times an variable is estimated
in the same dimension as originally estimated by an empirical
EGA structure or a theoretical/input structure.
The output also contains each variable's replication frequency (i.e., proportion of
bootstraps that a variable appeared in each dimension
Arguments
- bootega.obj
A
bootEGAobject- IS.plot
Boolean (length = 1). Should the plot be produced for
item.replication? Defaults toTRUE- structure
Numeric (length = number of variables). A theoretical or pre-defined structure. Defaults to
NULLor the empiricalEGAresult in thebootega.obj- ...
Deprecated arguments from previous versions of
itemStability
Value
Returns a list containing:
- membership
A list containing:
empirical— A vector of the empirical memberships from the empiricalEGAresultbootstrap— A matrix of the homogenized memberships from the replicate samples in thebootEGAresultsstructure— A vector of the structure used in the analysis. Ifstructure = NULL, then this output will be the same asempirical
- item.stability
A list containing:
empirical.dimensions— A vector of the proportion of times each item replicated within the structure defined bystructureall.dimensions— A matrix of the proportion of times each item replicated in each of thestructuredefined dimensions
- plot
Plot output if
IS.plot = TRUE
References
Original implementation of bootEGA
Christensen, A. P., & Golino, H. (2021).
Estimating the stability of the number of factors via Bootstrap Exploratory Graph Analysis: A tutorial.
Psych, 3(3), 479-500.
Conceptual introduction
Christensen, A. P., Golino, H., & Silvia, P. J. (2020).
A psychometric network perspective on the validity and validation of personality trait questionnaires.
European Journal of Personality, 34(6), 1095-1108.
See also
plot.EGAnet for plot usage in EGAnet
Author
Hudson Golino <hfg9s at virginia.edu> and Alexander P. Christensen <alexpaulchristensen@gmail.com>
Examples
# Load data
wmt <- wmt2[,7:24]
if (FALSE) { # \dontrun{
# Standard EGA example
boot.wmt <- bootEGA(
data = wmt, iter = 500,
type = "parametric", ncores = 2
)} # }
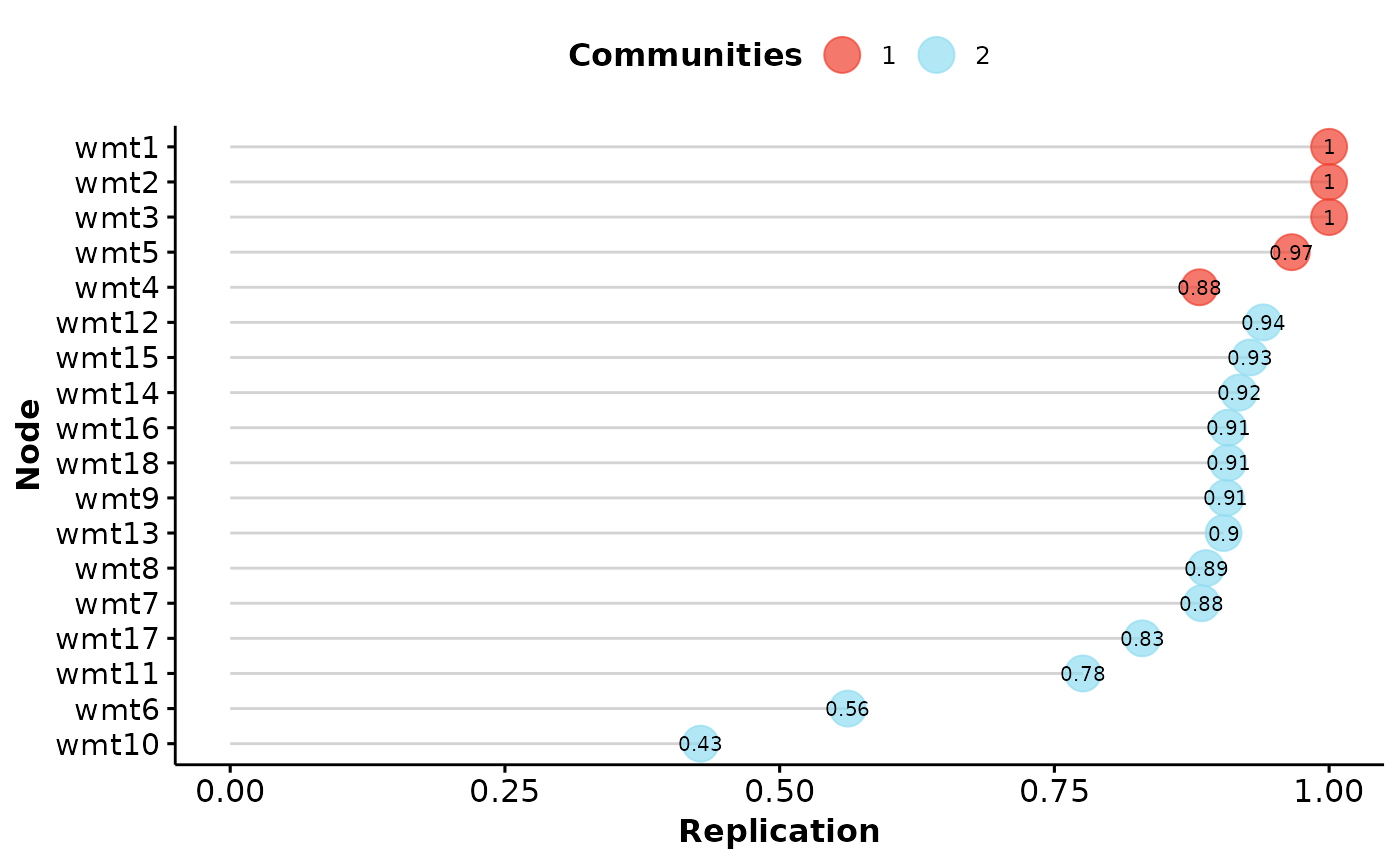
# Standard item stability
wmt.is <- itemStability(boot.wmt)
 if (FALSE) { # \dontrun{
# EGA fit example
boot.wmt.fit <- bootEGA(
data = wmt, iter = 500,
EGA.type = "EGA.fit",
type = "parametric", ncores = 2
)
# EGA fit item stability
wmt.is.fit <- itemStability(boot.wmt.fit)
# Hierarchical EGA example
boot.wmt.hier <- bootEGA(
data = wmt, iter = 500,
EGA.type = "hierEGA",
type = "parametric", ncores = 2
)
# Hierarchical EGA item stability
wmt.is.hier <- itemStability(boot.wmt.hier)
# Random-intercept EGA example
boot.wmt.ri <- bootEGA(
data = wmt, iter = 500,
EGA.type = "riEGA",
type = "parametric", ncores = 2
)
# Random-intercept EGA item stability
wmt.is.ri <- itemStability(boot.wmt.ri)} # }
if (FALSE) { # \dontrun{
# EGA fit example
boot.wmt.fit <- bootEGA(
data = wmt, iter = 500,
EGA.type = "EGA.fit",
type = "parametric", ncores = 2
)
# EGA fit item stability
wmt.is.fit <- itemStability(boot.wmt.fit)
# Hierarchical EGA example
boot.wmt.hier <- bootEGA(
data = wmt, iter = 500,
EGA.type = "hierEGA",
type = "parametric", ncores = 2
)
# Hierarchical EGA item stability
wmt.is.hier <- itemStability(boot.wmt.hier)
# Random-intercept EGA example
boot.wmt.ri <- bootEGA(
data = wmt, iter = 500,
EGA.type = "riEGA",
type = "parametric", ncores = 2
)
# Random-intercept EGA item stability
wmt.is.ri <- itemStability(boot.wmt.ri)} # }